On October 18, 2021, the Canadian Securities Administrators (CSA) proposed National Instrument 51-107 Disclosure of Climate-related Matters and its companion policy. As proposed, the rules would come into force on December 31, 2022 requiring reporting issuers, subject to limited exceptions and over a phased-in period, to disclose climate-related information in line with certain recommendations of the Taskforce on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). This marks a significant step forward in ensuring investors have access to consistent and comparable climate-related disclosure.
What you need to know
- The proposed rules would be phased-in over a one-year period for non-venture issuers and over a three-year period for venture issuers. For reporting issuers with a December 31 year-end, disclosures would be required in annual filings due in 2024 for non-venture issuers and in 2026 for venture issuers.
- Issuers would be required to make annual disclosure relating to the core elements of the TCFD framework, including governance, corporate strategy, risk management practices and data and metrics in respect of climate change risks and opportunities.
- Issuers would be required to disclose their Scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions1 or their reasons for not providing such disclosure. In the alternative, the CSA is considering mandatory disclosure of Scope 1 emissions, with the comply-or-explain option available only for Scope 2 and 3 emissions.
- The CSA has opted not to require disclosure of scenario analysis of a company’s resiliency under various climate transition assumptions.
- While studies have shown that many of Canada’s larger issuers, especially those included on the S&P/TSX Composite Index, are voluntarily disclosing some GHG emissions data, disclosure practices are mixed and many issuers are not currently disclosing Scope 3 emissions in part because of the challenges in third-party data collection and integrity.
- Many issuers will need to start planning now, as compliance with the proposed rules may require significant near-term investments of time and resources in data collection, risk analysis and assessment of governance systems.
- Comments on the proposed rules are due by January 17, 2022.
Background
Canadian securities laws currently require disclosure of certain material climate-related information in an issuer’s regulatory filings. The CSA has previously published guidance for public companies in preparing this disclosure—most notably Staff Notice 51-358, as discussed in our August 2019 bulletin. However, pressure has been building internationally and in Canada to mandate consistent and comparable climate-related disclosure requirements for public companies.
Internationally, the Financial Stability Board established the TCFD to promote more effective climate-related financial disclosures through existing reporting practices. The TCFD released its final recommendations in 2017, setting out a voluntary framework for companies to organize their climate disclosure around four main topics: “governance”, “strategy”, “risk management” and “metrics and targets”.
In several countries, the TCFD’s recommendations are quickly evolving into mandatory requirements. The United Kingdom already requires certain premium listed companies to either comply with the TCFD’s recommendations, or explain why they have not, and is proposing to phase-in mandatory TCFD-aligned reporting for all registered companies beginning in 2022. In the U.S., the Securities and Exchange Commission recently undertook a consultation on climate change disclosure, including on whether the Commission should consider rules that adopt the TCFD recommendations.
At home, the Canadian government has announced its support for the TCFD, and Ontario’s Capital Markets Modernization Taskforce recently recommended that all non-investment fund reporting issuers be required to provide, to the extent material, TCFD-aligned disclosures relating to governance, strategy and risk management, as well as GHG emissions data on a comply-or-explain basis2.
Meanwhile, investor and stakeholder pressure has been building for consistent and comprehensive climate-related disclosure. Shareholder proposals have increasingly targeted better reporting on companies’ climate action plans and GHG emissions reduction targets, while several high-profile lawsuits have sought to force companies to improve their climate disclosure practices.
To date, Canada ranks behind the UK and Europe, and roughly on par with the US, in the percentage of public companies that are disclosing their GHG emissions and in setting climate-related targets3.
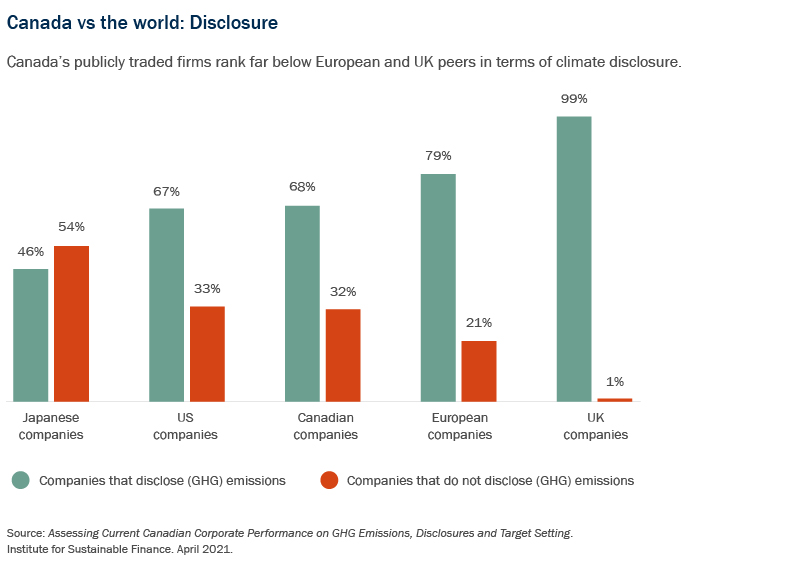
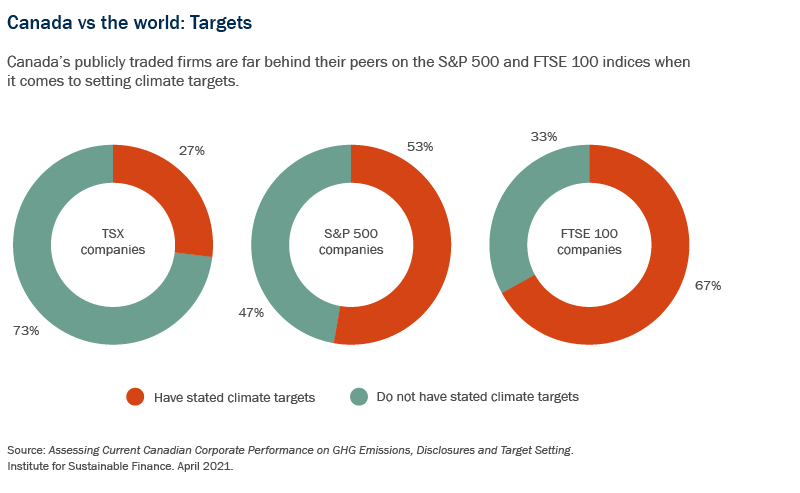
The TCFD recommends disclosure of metrics and targets used to assess climate-related risks and opportunities, together with information on climate-related governance, strategy and risk management. The CSA notes that while Canadian public companies have generally improved their climate-change disclosure in recent years, disclosures are frequently boilerplate, vague or incomplete, that risk disclosures often fail to address financial impact, and that no disclosures quantify that impact.
By requiring TCFD-aligned disclosure, the proposed rules would also bring alignment to reporting methodologies in an area where there remains many different standards and frameworks, despite recent harmonization efforts. According to the CSA, based on a review of 48 selected large Canadian issuers primarily from the S&P/TSX Composite Index, issuers use on average three voluntary frameworks to guide their climate-related disclosure (namely, GRI, SASB and TCFD), with 55% of those disclosures referencing the TCFD recommendations.
Summary of the proposed rules
The proposed rules would apply to all reporting issuers other than investment funds, issuers of asset-backed securities, designated foreign issuers, SEC foreign issuers, certain exchangeable security issuers and certain credit support issuers. The rules would be phased-in as follows (assuming a December 31, 2022 effective date):
- Non-venture issuers: one-year transition phase. Issuers with a December 31 year end would need to comply in their annual filings due in 2024 (in respect of fiscal 2023).
- Venture issuers: three-year transition phase. Issuers with a December 31 year end would need to comply in their annual filings due in 2026 (in respect of fiscal year 2025).
The proposed rules require climate-related disclosure that covers the TCFD’s core recommendations, as follows:
|
Required disclosure |
Location of disclosure |
|---|---|
|
Governance |
|
|
Describe the following:
No materiality threshold. |
Management information circular (MIC) If no MIC, annual information form (AIF) If no MIC or AIF, annual MD&A |
|
Strategy |
|
|
Describe the following, where such information is material:
|
AIF If no AIF, annual MD&A |
|
Risk management |
|
|
Describe the following:
No materiality threshold. |
AIF If no AIF, annual MD&A |
|
Metrics and targets |
|
|
Disclose:
* In the alternative, the CSA is considering mandatory disclosure of Scope 1 GHG emissions and a comply or explain regime for disclosure of Scope 2 and 3 GHG emissions only. |
AIF If no AIF, annual MD&A |
In contrast to the TCFD’s recommendations, the proposed rules would not require reporting issuers to disclose a scenario analysis of their resiliency under various climate transition assumptions. The CSA acknowledged that this analysis is complex and can vary widely between issuers, making it difficult for investors to analyze. In response to its recent climate change discussion paper, OSFI received similar feedback, with many respondents highlighting the difficulty in developing robust climate change scenarios. This may change over time as companies improve their capacity to evaluate their sensitivity to climate-related risks.
In preparing the required disclosure, issuers would only need to disclose material information, with certain important exceptions. The proposed rules would require TCFD-aligned disclosure relating to “governance” and “risk management”, without any materiality assessment, consistent with disclosure requirements for corporate governance matters under NI 58-101.
The CSA reminds issuers that the proposed rules may require disclosure that constitutes forward-looking information (FLI) which must comply with existing Canadian securities law requirements, namely that the issuer has a reasonable basis for disclosure of the FLI, that material FLI be identified as such, that it be accompanied by appropriate cautionary disclosure regarding the risks and assumptions underlying such FLI and that the issuer describe its policy for updating the FLI. Given the longer-term and variable nature of climate change disclosures, issuers should consider whether their current safe harbor language is robust enough to address the risks and assumptions that may be unique to climate change reporting.
Current state of TCFD-aligned disclosure and next steps
In recent years, an increasing number of issuers have expanded their climate-related disclosures. However, the CSA and others have identified inconsistencies in the detail and coverage of this information. Many companies have yet to align their disclosure with the TCFD framework. According to the TCFD’s October 2021 report on the status of climate-related disclosures:
- Less than 26% of the companies in the review group were meeting the TCFD’s disclosure recommendations in respect of “governance”;
- Less than 53% were meeting the recommendations in respect of “strategy”;
- Less than 31% were meeting the recommendations in respect of “risk management”; and
- Less than 45% were meeting the recommendations in respect of “metrics and targets”4.
Although the proposed rules would only take effect on December 31, 2022, and be phased-in after that date, many issuers will want to seize the opportunity now to collect appropriate GHG emissions data, evaluate climate-related risks and opportunities and implement the corporate strategy and governance systems necessary to ensure accurate and compelling disclosure when the requirements come into force. As a starting point, boards and management should examine their current climate-related governance structure and disclosure and develop an understanding of the information and data that is available, and where there are gaps. In addition, issuers that currently release voluntarily climate-related disclosure in sustainability reports, ESG reports or other non-core filings should undertake a process to identify the climate change disclosure in those filings that might be integrated into their core documents to satisfy the proposed rules. These steps, among others, will help issuers position themselves for compliance in the future.
Learn more about our Capital Markets and ESG work.
- Under the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, the leading corporate GHG reporting protocol, Scope 1 emissions are direct GHG emission from sources that are owned or controlled by a company; Scope 2 emissions are GHG emissions resulting from the generation of purchased electricity consumed by the company; and Scope 3 emissions are all other indirect emissions that occur as a consequence of the company’s activities, a very broad category that may include the emissions of a company’s investments and supply chain.
- For further information, please see our February 2021 bulletin.
- See the “Assessing Current Canadian Corporate Performance on GHG Emissions, Disclosures and Target Setting”, Institute for Sustainable Finance, Smith School of Business, Queen’s University (April 2021), Figures 2 and 5.
- See Figure B2 of the report for further detail. For this report, the TCFD reviewed the 2020 disclosures of 1,651 public companies.
To discuss these issues, please contact the author(s).
This publication is a general discussion of certain legal and related developments and should not be relied upon as legal advice. If you require legal advice, we would be pleased to discuss the issues in this publication with you, in the context of your particular circumstances.
For permission to republish this or any other publication, contact Janelle Weed.
© 2025 by Torys LLP.
All rights reserved.
Tags
Capital Markets
Transactions
Sustainability
Environmental
Government and Crown Corporations
Advisory and Regulatory
Board Advisory and Governance
Activism and Defence
Banking and Debt Finance
Projects
Infrastructure Energy and Resources
Oil and Gas
Mining and Metals
Infrastructure
Power and Renewable Energy
Industrial and Manufacturing
Transportation


